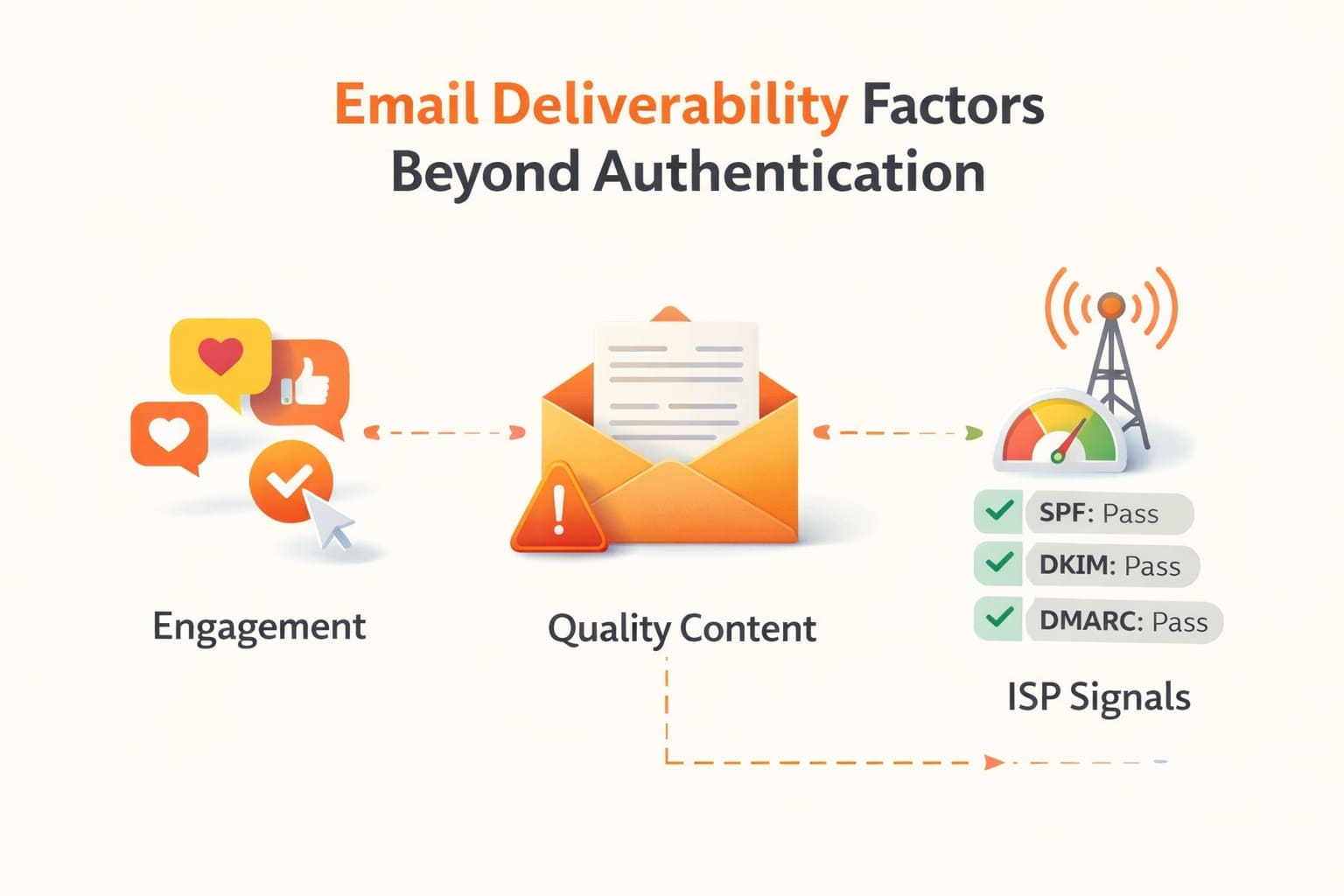
Email Deliverability Factors Beyond Authentication (Engagement, Content & ISP Signals)
Explore the key deliverability factors beyond SPF, DKIM, and DMARC including engagement signals, content quality, sending reputation and ISP filtering influences.
Introduction
Many senders focus solely on SPF, DKIM, and DMARC when optimizing email deliverability. While authentication is critical, inbox placement is influenced by additional signals that go far beyond these protocols.
Understanding these extra factors helps businesses improve email performance and avoid filtering by major Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
Engagement Signals from Recipients
Modern mail providers such as Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo evaluate how users interact with your emails. Positive engagement signals usually result in better inbox placement, while poor engagement can signal spammy behavior.
- Open rates
- Click-through rates
- Replies and forwards
- Marking as “Not spam”
Low engagement can send a strong negative signal, even if DKIM, SPF, and DMARC are correct. 📊 ISPs use this feedback to decide where future emails should land—**inbox vs spam**.
Quality of Email Content
Spam filters assess both syntax and content quality. Emails with certain content patterns trigger filters, including:
- Overuse of promotional language
- Too many links or lack of text balance
- Suspicious attachments or macros
- Misleading subject lines
Keeping content relevant, clean, and well-formatted improves reputation with spam engines and boosts deliverability.
Sending Frequency & Consistency
Sudden spikes in sending volume or inconsistent sending patterns can make ISPs suspicious. A steady, predictable email cadence signals a legitimate sender.
This is especially important for newsletters, transactional emails, and mass campaigns. Consistency builds **sender trust over time**.
Infrastructure & Reputation Signals
Aside from authentication, the overall reputation of your sending infrastructure matters. Tools you already use on this site help diagnose and improve these foundational elements:
- IP Reputation Checker – evaluate trustworthiness of sending IPs
- Blacklist Checker – detect blacklist status
- Complete Email & IP Audit – comprehensive deliverability assessment
High sending reputation combined with clean infrastructure fosters better deliverability.
ISP Filtering Rules & Machine Signals
ISPs analyze billions of signals in real time. Beyond authentication, they monitor behavior patterns, content consistency, and even **machine-learning based anomaly detection** to evaluate email risk. AI-powered filters adapt continuously to new threat signals. :contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}
User Complaints & Spam Reports
If recipients frequently mark your emails as spam or delete them without opening, this generates negative signals. These complaints can drastically reduce deliverability and overall sender score.
Best Practices for Full Deliverability Success
To maximize inbox placement, combine the following practices:
- Validate SPF, DKIM, and DMARC (use authentication checkers above)
- Monitor engagement metrics and improve content relevance
- Send consistently and avoid sudden volume spikes
- Ensure clean IP reputation and blacklist absence
- A/B test subject lines and send times for optimal engagement
Conclusion
Authentication is just the foundation. For consistent inbox placement, you must optimize engagement, content quality, infrastructure reputation, and user interactions. By monitoring these deliverability signals and using targeted tools, both technical and behavioral factors are addressed, ensuring better email performance and user trust.